Coquitlam embraces FME for 20+ years
In British Columbia, the City of Coquitlam has been leveraging FME for over 20 years to support city initiatives, including a recent focus on implementing legislative housing mandates. FME’s seamless integration with Esri and other GIS environments has made the tool a crucial part of their data management, enabling them to address various challenges effectively. The team’s mission is to transform data into actionable insights, aiding in efficient decision-making processes.
Leveling up urban planning with the Community Baseline tool
The Community Baseline tool integrates data from numerous sources, providing a GIS interface for staff to access and utilize asset data crucial for land use and servicing decision-making. With the province’s frequent updates in planning legislation, the City plans to use the Community Baseline tool to support servicing impact assessment of legislative amendments.
The tool collates and visualizes massive datasets, including BC assessment data and utility model data, helping city staff identify opportunities for encouraging land use density. Using FME, the team effectively manages these large datasets, aligning them in a unified platform easily accessible and interpretable by various city departments.
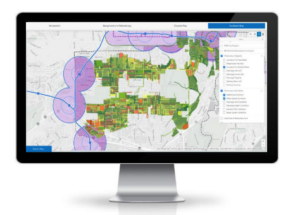
Enhancing interdepartmental collaboration
The success of the Community Baseline tool highlights the power of collaborative efforts. By bringing together data from multiple sources, including components of asset management and land use planning, the tool facilitates comprehensive development planning. It provides insights into significant constraints and opportunities for development, serving as a critical component in strategic planning for infrastructure and resource allocation. The visualization capabilities of the tool allow for easy analysis and understanding of complex asset data, serving as a critical source for data-driven decisions that shape the city’s future.
The platform interface includes data surrounding redevelopment likelihood, average land values, utility information, and more. New model data is fed into the tool, and FME generates the necessary information. Generating a population estimate would have previously taken someone a week to manually review a few blocks; the entire city can now be run in about 60 seconds, a feat that would have been impossible to achieve without FME.
The success of the Community Baseline has been attributed to the collaborative approach used throughout its design and development. Bringing together workflows and data from multiple departments and bringing staff together in positive and effective ways reinforces how GIS encourages collaboration across departments to meet the organization’s challenges. Engineering and Planning & Development Planning staff continue to rely on this relevant tool that enables more efficiencies in their day-to-day operations. The success of the Community Baseline has been so widely acknowledged that the City has been approached by other municipal organizations looking to undertake a similar project.
Powering the new e-scooter program
FME’s impact extends across various city operations. In urban mobility, FME has streamlined the analysis of e-scooter program data, integrating statistics from two providers into a single dashboard. The chosen pilot scooter companies must provide the city with statistics such as the number of trips and unique riders to the project managers. The Micro-Mobility team was asked to combine the data into a single internal dashboard to simplify data calculations.
FME allows visibility into all of the scooters available in the city in near real-time, and averages the number of uses per day, allowing the team to see how many trips per vehicle happened daily. This efficiency saves roughly 4 hours a week by negating the need for staff to manually search for data in various platforms. They can now look at all the necessary data in seconds enhancing their ability to monitor and adjust the program effectively.

Streamlining operations across departments
The team is also using FME to coordinate garbage cart exchanges so the public can change their garbage can sizes. Garbage cart exchanges are collected and managed within the City’s work order management system, and the public is responsible for that cost, but the system lacks an online payment capability. FME is used to push that data into their permanent system to allow for online cart exchange payments, integrating with Maximo and Amanda. Customers no longer need to visit city hall to pay for cart exchanges, improving customer service.
The City is also using FME for vehicle inspections, using ArcGIS Online to collect inspections by field staff, and FME to push the data into their work order management system. Any vehicle issues found during inspection trigger an automatic service request creation. Vehicle inspections were previously paper-based, and the inspectors would have to come to the office to report issues for manual review and management. By going paperless, they can keep better records and remove duplicate entries.
Future prospects and ongoing impact
Looking ahead, the Community Baseline tool will continue to evolve with FME at its core. The tool will play a crucial role in long-term monitoring and impact assessment of urban development projects. With FME, the team is equipped to promptly handle new legislative requirements and business needs, maintaining their agility in urban management.
FME’s robustness and adaptability have eliminated data barriers and fostered a culture of confidence and innovation within the Coquitlam team. The ability to handle complex datasets and integrate them across various platforms and departments has reinforced FME’s essential role in Coquitlam’s ongoing success in data-driven governance.
The City of Coquitlam’s extensive use of FME demonstrates its significance in the city’s strategic planning and operational efficiency. As Coquitlam continues to navigate the complexities of urban development, FME remains a crucial part of powering informed, strategic, and impactful decisions.




